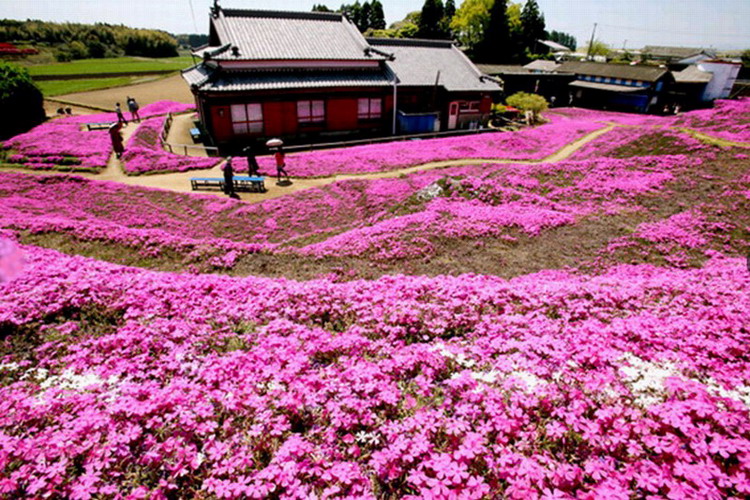
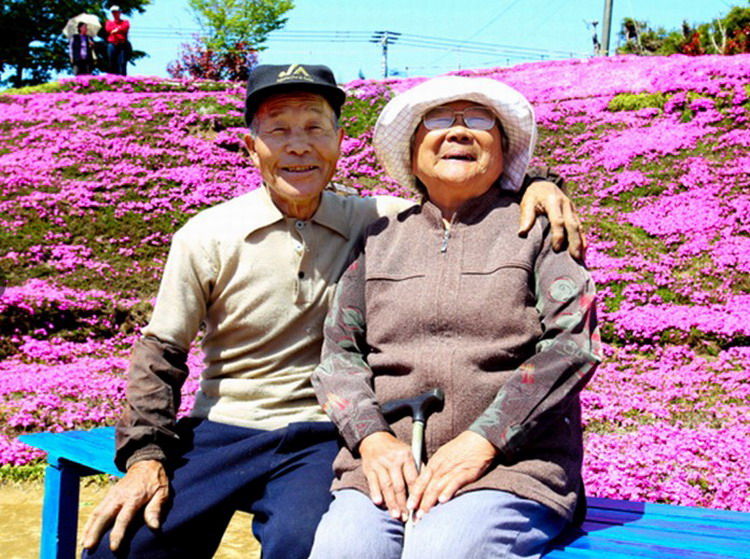
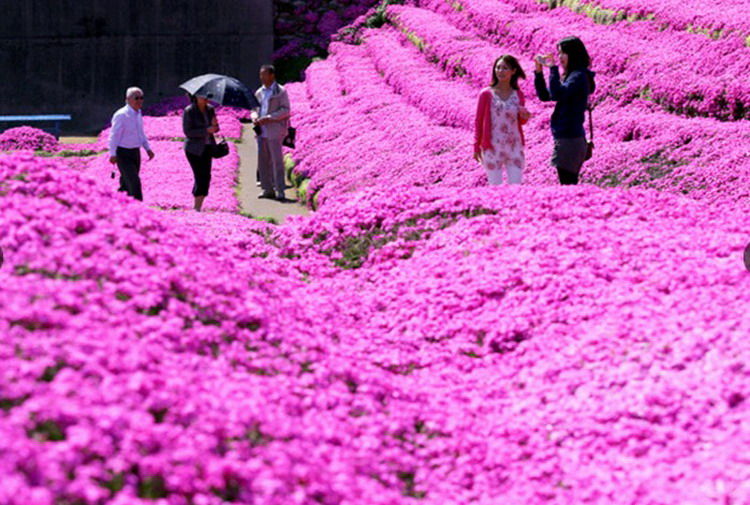
位處柴灣的東區尤德夫人那打素醫院, 由主座大堂地下前往東座的通道上, 有一個地方寬闊的表演, 展覧場地, 活躍醫院的人愛稱呼這地方叫” 红館 “.
這天心情有點雀躍, ( 微電影, 我們的真實故事 ) 得到管理人員的支持, 我們终於可一嚐踏足红館的滋味, 在這裡展出這系列作品的劇照並播放電影. 红館是前往腫瘤科覆診的必經通道, 而作品展示地點光缐充裕, 又有足夠的空間讓途人駐足欣賞, 每一個微细的環節也教我喜出望外, 當我在現場佈置展覽的時候, 一方面感到滿心欣喜, 一方面實實在在感受得到, 什麽是世事如棋………….
我和幾位家人, 也曾是東區醫院的常客. 這些年一直忙這忙那, 早已經將定期覆診的事抛諸腦後. 正好藉著這次展覧頻繁出入醫院的方便, 重返久違了的腫瘤科约期並安排抽血. 按記錄顯示, 原來有兩年沒有回來了, 負責抽血的護士站姑娘十分仔细核對資料, 一邊略帶責怪一邊出自關心的説 : “這麽重要的事也可以忘記的……..”
是的, 我確實沒放這事在心上, 畢竟和癌症分手已十數年, 莫説今天, 即使我患病的幾年, 也沒有特別將這件事看得太重. 並不是我對生死毫不著緊, 是那幾年衝擊我們家庭的風浪畢竟太大了.
話説病癒後重返工作崗位的我, 搖身一變成為一位任重道遠的照顧者, 源於我老爸和大姐也病重了, 素來我們親友已不多, 老媽亦年事已高, 偏偏我三哥, 四姐早前也相繼癌症病發, 我們突然之間由一個平凡的小家庭變得不合情理的悲慘.
記起某年某日, 就在東區醫院.正座6/F病房的兩端, 躺在病床上的一方是老爸, 遠遠的另一方是大姐, 當我下班趕來陪伴硬朗的老媽遊走病房之間探訪的時候, 有個許多荒誕的影像在腦内徘徊, 如果這是電視劇本的情節恐怕會被網民咒駡煽情得不合常理, 但這是事實.
今日回想起來, 故事中另外的三人到底在想什麽 ?
關於我大姐是如何想, 不用猜測太多, 因當時她已經神智不清, 距離她旅程的终结已不遠. 老爸, 一次又一次和癌症擦身已過, 最终仍是逃不掉, 然後手術的意外….; 老媽心靈上一再受創, 或許上天也不忍, 給予她一次毫無先兆的無痛結束, 今天, 他們也是故人了, 對於我來説, 感覺上也差不了多少, 當你十分瞭解某一個人的思想與言行時, 不論身處何方, 何時何地, 你會知道他的選擇, 你會估計到她將會説什麽, 你會不期然地感受得到, 他原來一直生活在你身邊.
(待續 )
编輯(